How Shot Blasting Machines Work
Shot blasting machines are integral to various industries for cleaning, strengthening, and polishing metal surfaces. Understanding how these machines operate helps in appreciating their efficiency and versatility. This detailed overview explains the working principles of shot blasting machines, including the key components and processes involved.
Working Principle of Shot Blasting Machines
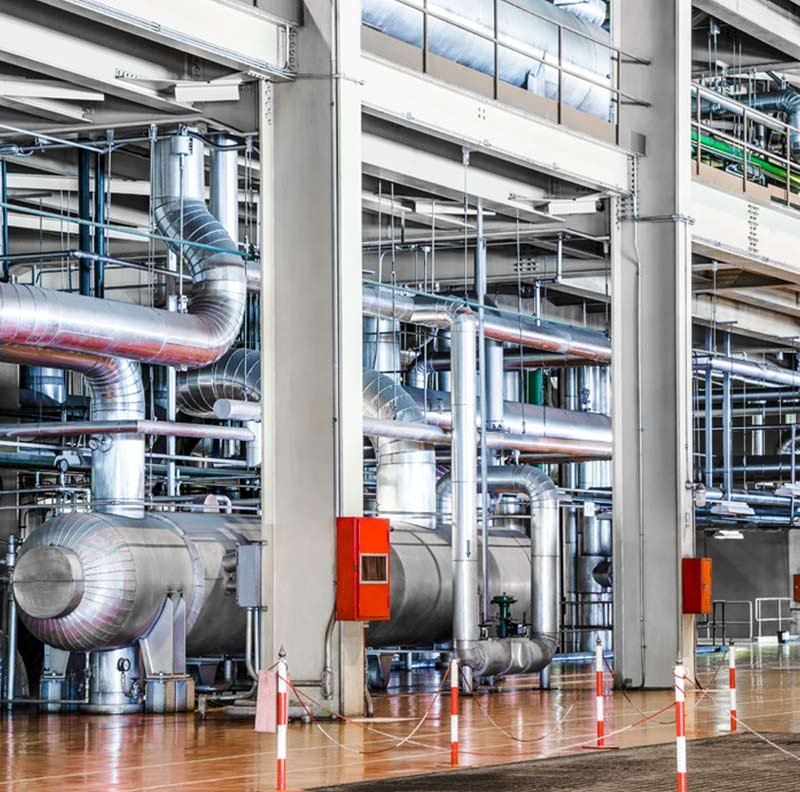
Shot blasting machines operate by mechanically propelling abrasive media at high velocity towards the surface of a workpiece. The impact of the abrasive material removes contaminants, scales, or coatings, leaving the surface clean and prepared for subsequent processing.
Key Components and Their Functions
- Blast Wheel
- Function: The blast wheel is the heart of the shot blasting machine. It converts electrical energy into kinetic energy, propelling the abrasive media towards the workpiece.
- Components: The blast wheel consists of blades, an impeller, and a control cage. The control cage regulates the flow and direction of the abrasive media, ensuring it hits the workpiece at the correct angle and speed.
- Abrasive Media
- Function: The abrasive media, such as steel shots or grits, is the material that actually contacts and cleans the workpiece.
- Types: Common abrasive media include steel shots, steel grits, aluminum oxide, and glass beads. The choice of media depends on the desired finish and the material of the workpiece.
- Blasting Chamber
- Function: The blasting chamber is the enclosed space where the blasting operation occurs. It contains the blast wheel and the workpiece, protecting the surroundings from the abrasive action.
- Design: The chamber is lined with wear-resistant materials to withstand the constant impact of the abrasive media.
- Dust Collector
- Function: The dust collector ensures a clean working environment by capturing dust and debris generated during the blasting process.
- Types: Common types include cartridge filters and cyclone separators, which efficiently filter out particulate matter from the air.
- Elevator and Separator
- Function: The elevator lifts the used abrasive media to the separator, where reusable media is separated from waste materials.
- Process: The separator uses air flow and screens to clean the media, which is then recycled back into the blasting cycle.
Step-by-Step Shot Blasting Process
- Loading the Workpiece
- The workpiece is loaded into the blasting chamber. Depending on the type of machine, it may be placed on a conveyor, hung on hooks, or placed in a rotating drum.
- Blasting Operation
- The blast wheel propels the abrasive media at high speed towards the workpiece. The impact of the media removes rust, scale, paint, or other contaminants from the surface.
- The workpiece may be rotated or moved within the chamber to ensure even coverage and thorough cleaning.
- Media Recovery
- The used media, along with debris and contaminants, falls to the bottom of the chamber. The elevator lifts this mixture to the separator.
- The separator cleans the media, removing dust and broken particles. The cleaned media is returned to the blast wheel for reuse.
- Dust Collection
- Throughout the process, the dust collector captures fine particles and dust, maintaining a clean environment and preventing contamination of the workspace.
- Unloading the Workpiece
- After blasting is complete, the clean workpiece is removed from the chamber, ready for further processing such as painting, coating, or assembly.
Types of Shot Blasting Machines and Their Operation
- Tumble Blast Machines
- Operation: Workpieces are loaded into a rotating drum. As the drum tumbles, the blast wheel propels media, cleaning the surfaces uniformly.
- Application: Ideal for small to medium-sized workpieces in bulk, such as castings and forgings.
- Spinner Hanger Machines
- Operation: Workpieces are hung on hooks and rotated through the blast stream. The rotation ensures all sides are cleaned.
- Application: Suitable for larger, more complex workpieces, like automotive parts and heavy machinery components.
- Continuous Blast Machines
- Operation: Workpieces are continuously fed through the machine on a conveyor system. The blast wheel cleans the surfaces as they pass through.
- Application: Perfect for high-volume production lines, ensuring consistent quality and efficiency.
- Table Blast Machines
- Operation: Workpieces are placed on a rotating table within the chamber. The blast wheel targets the surfaces as the table turns.
- Application: Used for larger, flat workpieces, such as steel plates and welded structures.
Conclusion
Shot blasting machines are vital for preparing and finishing metal surfaces in various industrial applications. By understanding the components and working principles, businesses can optimize their use, ensuring efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly surface treatment processes. Whether cleaning, deburring, or enhancing the mechanical properties of metal parts, shot blasting machines provide a versatile and powerful solution for maintaining high-quality standards in manufacturing and maintenance operations.
Factors That Affect Shot Blasting Efficiency
Certifications to Look for in Shot Blasting Machine Manufacturers
Different Types of Sand Blasting Machines and Their Functions